

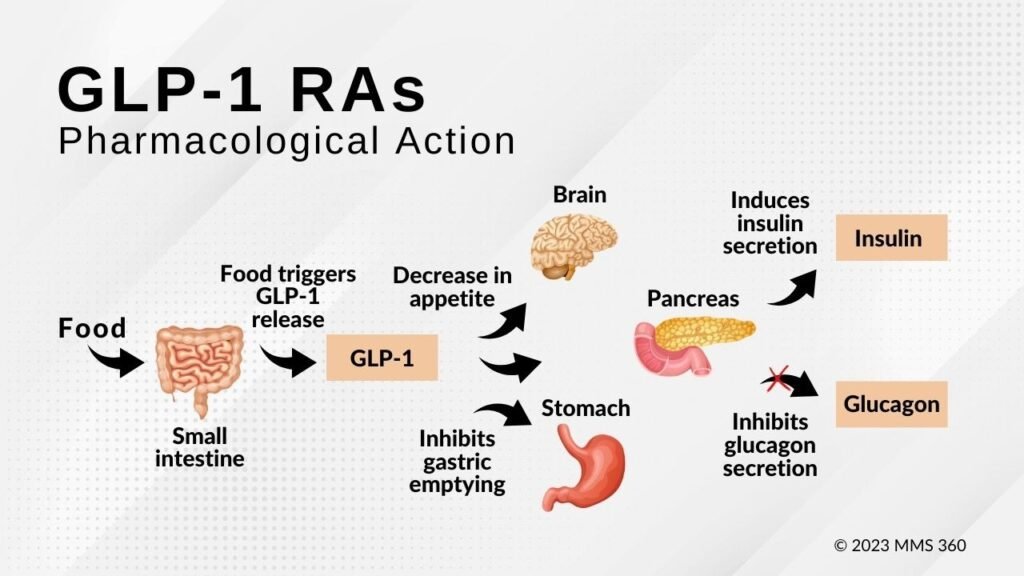
Semaglutide, functioning as a GLP-1 receptor agonist, exerts specific effects on various organs, encompassing the small intestine, stomach, pancreas, and brain. Here’s a comprehensive examination of its actions on each organ:
Small Intestine:
1. Incretin Effect: Semaglutide amplifies the incretin effect, triggering the release of hormones in response to food consumption. Within the small intestine, it boosts the secretion of incretin hormones (such as GLP-1) following nutrient ingestion.
2. Nutrient Absorption: While semaglutide enhances the incretin effect, its primary impact lies in hormone secretion rather than direct modulation of nutrient absorption processes within the small intestine.
Stomach:
1. Gastric Emptying: Semaglutide decelerates gastric emptying, resulting in delayed movement of food from the stomach to the small intestine. This delay prolongs feelings of fullness, aiding in the reduction of overall food intake and supporting weight loss or management in obesity treatment.
2. Appetite Regulation: The slowed gastric emptying influenced by semaglutide also affects appetite signals, partially regulating appetite based on the pace at which the stomach empties its contents.
Pancreas:
1. Insulin Secretion: Semaglutide prompts the beta cells in the pancreas to increase insulin production in response to elevated blood glucose levels. This mechanism assists in lowering blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes.
2. Glucagon Suppression: Additionally, semaglutide inhibits the release of glucagon from the alpha cells in the pancreas when blood sugar levels are low. By suppressing glucagon, which typically elevates blood sugar levels, this medication helps maintain a more stable glucose level.
Brain:
1. Appetite Control: Semaglutide influences the appetite centers in the brain, leading to a reduction in hunger and calorie consumption. This effect proves advantageous for weight management in individuals with obesity.
2. Satiety Signals: Moreover, semaglutide enhances satiety signals in the brain, fostering a sensation of fullness and assisting in portion control and overall food intake reduction.
Benefits:
Clinical Trials and Research: Numerous clinical trials have validated the efficacy and safety of Semaglutide. Studies have shown significant reductions in HbA1c levels and weight loss, making it a critical option for those struggling with diabetes and obesity. Ongoing research continues to explore additional benefits and long-term outcomes of this medication.
Side Effects and Considerations: While it is effective, it can have side effects including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. It’s important to discuss these potential side effects with your healthcare provider.
Usage and Dosage: Typically administered once a week via subcutaneous injection. Dosage and administration should be personalized based on individual medical conditions and response to treatment.
Conclusion: It offers a comprehensive approach to weight and diabetes management, making it a promising option for individuals seeking effective treatment strategies. By understanding its mechanisms and benefits, patients can better appreciate its role in improving health outcomes.
To learn more about this treatment and its benefits, or to schedule a consultation, contact Kairos Health and Wellness today.